Euro used since 2002 in The Eurozone, the currency of 19 EU members. There are three types of banks in the country, namely private commercial banks, public sector banks and cooperative banks. Also, the number of online banks is increasing. Deutsche The Bundesbank is the country's central bank and the authority that regulates the German banking industry, The Federal Financial Supervisory. Provided by Authority ( BaFin ). Private commercial banks in Germany have the largest share of assets and play an important role in the export economy.
Private commercial banks are among the banks with the largest share of assets in the industry, accounting for 40% of assets. The competition rate among these banks is quite high and they are also in competition with each other. They play an important role in the export economy in Germany and finance a large part of international trade. According to the European Banking Federation's December 2022 report, they account for 88% of Germany's exports and control almost three-quarters of the German external network. Deutsche Bank is the largest among banks in this category and is the 11th largest bank in the world. The three largest banks in Germany are Deutsche Bank, Commerzbank and KfW, respectively. However, banks in this category are not as influential in the retail banking sector, with the three largest private commercial banks controlling only 15% of the retail banking sector.
In Germany, public banks consist of savings banks ( Sparkassen ), Landesbanken and DekaBank . DekaBank operates as the asset manager of the Savings Banks Finance Group. Public banks account for 25% of total banking assets and there are 371 savings banks in Germany. Savings banks are often organized as public law firms with their guarantors or owners and local governments, and their areas of influence are usually limited to those of local government. Savings banks do not compete with each other. Landesbanken was originally established as a central bank for savings banks, but in recent years they have become more involved in wholesale finance, investment banking and international business activities and have begun to rival commercial banks. In Germany, 6 Landesbanken belongs to the federal states and to the regional associations of savings banks.
The cooperative sector in Germany consists of 773 cooperative banks ( Volks - und Raiffeisenbanken ) and a central cooperative bank called DZ Bank AG. Cooperative banks constitute 53% of bank institutions and 12% of bank assets. These banks are usually managed by their own members, depositors and borrowers. Legally, such banks are authorized to support their members, who are half of their customers. They also provide banking services to the public. Cooperative banks, like savings banks, are regional and act on regional principles.
Cooperative and public banks are seen as more reliable and less risky than private commercial banks. Some cooperative banks have begun to pursue outward-looking strategies. Both types of banks cater more to local communities than to international visitors.
German banks, like other European countries, offer large-scale financial services. These services include current accounts, loans and overdrafts, mortgages, insurance, investment and savings accounts, digital and online banking, business banking and services for foreigners. Business banking is the set of financial services offered by German banks for start-up companies, established SMEs and multinational or individual employees doing business in Germany. German banks also offer special services for foreigners working in Germany, including cheap international money transfers.
Germany is the country with the highest Turkish population in Europe. According to the 2022 data from the German Federal Statistical Office, 1 million 458 thousand 360 Turkish citizens live in Germany. This figure does not include the number of Turks who acquired German citizenship. This high population number makes Turkish banking activities more active in Germany. The use of Turkish banks by Turks living in Germany has some advantages. Among them:
Banks to provide service in Turkish : Turkish banks provide services using the mother tongue of Turks living in Germany. In this way, it is possible for Turks to carry out their financial transactions in a more comfortable and understandable way.
Lower transfer fees : Money transfers between Turkish banks can usually be made with lower fees. This allows Turks to spend less on sending the money they earn in Germany to Turkey.
More favorable loan and interest rates for Turks : Turkish banks offer loan and financing packages specially prepared for Turks. Interest rates on these packages are also usually lower. This enables Turks to use loans on more favorable terms.
Some Turkish banks actively operating in Germany are:
» Isbank AG
İşbank is the first Turkish bank to open branches in foreign countries. It opened its first branch in Hamburg in 1932, but this branch was closed due to World War II. Later, it started its activities again in Frankfurt in 1976.
» Ziraat International Bank AG
Ziraat Bank AG is the largest private bank with Turkish capital in Germany and the European Union, with an equity of 250 million dollars. It opened its first representative office in Germany in 1964 and established its first branch in Frankfurt in 1988.
» DenizBank AG
DenizBank opened its first branch in Austria in 1996. It currently has an active branch network and 400 employees in Austria and Germany.
» GarantiBank International N.V.
GarantiBank opened its first branch in the Netherlands in 1990. It opened its first branch in Germany in 1999.
» Akbank AG
Akbank started its operations in 1998 in Frankfurt, Germany. In addition, the bank is the Deposit Protection Fund of the German Banks Association
Einlagensicherungsfonds. des Bundesverband Deutscher He is a volunteer member of Banken.
» KuveytTurk - KT Bank AG
KT Bank AG is the first bank in Germany and the Eurozone to offer services in accordance with the principles of participation banking since 2004. The headquarters of the bank is in Frankfurt/Germany.
» Credit Europe Bank
It is a bank of Turkish origin. Although the headquarters of Credit Europe Bank is located in Amsterdam, the origins of bank are based in Turkey. The bank was
established in Turkey in 1994 and its name was changed to Credit Europe Bank in 2006. Credit Europe Bank also has several branches in Germany and offers banking services in Germany as well. Credit Europe Bank offers credit cards, deposit accounts, investment accounts, online banking, international money transfers, consumer loans and other financial services in Germany. Today, Credit Europe Bank's operations in Turkey are transferred to Credit Europe Bank A.Ş. under the name.
Banks in Germany are divided into three separate groups. These are private banks, publicly owned savings banks ( Landesbanks ) and member-owned credit unions. The German banking system consists of approximately 1,800 banks, including 200 private banks, 400 public banks and 1,100 member-owned credit unions. There are also many foreign banks and financial institutions that are not headquartered in Germany but operate in Germany. For this reason, Germany is considered one of the largest banking centers in the world.
German banking is active in Turkey both through its representative offices and branches. Among the German banks with representation in Turkey, Aareal Bank AG ., Commerzbank AG, DEG- Deutsche Investitions-und Entwicklungsgesellschaft MBH, DZ Bank AG, KFW (Kreditanstalt Für Wiederaufbau) and the Landesbank Baden are located in Württemberg . The only German bank with a branch in Turkey is Deutsche Bank , which was established in 1987 and this bank only offers corporate banking services. In addition, although Hypovereinsbank does not have a representative or branch in Turkey, it cooperates with Yapı Kredi Bank.
Consolidation plays an important role in scaling the German economy. One of the most common causes of consolidation between savings banks and cooperative banks is stress. There may be more consolidation pressure in the coming years due to factors such as the low interest rate environment and banking regulations that have increased the capital needs of banks in recent years. German banks are particularly concerned that corporate finance may be affected and the lending capacity of banks may be restricted. However, according to the European Banks Association (EBF) data, loans extended to companies and self-employed individuals, accompanied by low interest rates and favorable financing conditions, increased by 4.3% in 2019 compared to the previous year and reached 974 billion Euros. Due to the Energy
Transition in Germany and the new EU Action Plan 'Financing Sustainable Growth ', banks have launched many initiatives to promote sustainable finance in recent years.
The European Central Bank (ECB) aims to increase investment and long-term loan demand in Germany with negative interest rates and large purchasing programs. The ECB seeks to achieve this goal by lowering rates along the entire yield curve. However, negative ECB rates reduce bank profitability, as banks cannot largely pass negative rates to customers. This situation also weakens the lending capacity of banks in the long run. The ECB's massive buyout programs are causing a sharp increase in excess liquidity in the banking system.
In conclusion, several important points regarding Germany's financial system stand out. Germany stands out as a country with a well-developed financial services infrastructure and serves bank loans as well as capital markets. Bank loans are an important source of finance, especially for small and medium-sized firms known as Mittelstand. However, factors such as low interest rates and excess liquidity reduce banks' profitability and weaken their long-term lending capacity. Banks are expected to take measures such as consolidation to cope with these challenging conditions and take initiatives to promote sustainable finance.
Share:
Related Articles

Healthy Growth: Why Organizations Sl ...
Companies want to grow. More market share, higher revenues, larger organiza ...

Sustainable Leadership: Power Built ...
Today, the concept of sustainability sits at the center of almost every str ...

Why Do Managers Struggle with Genera ...
A reality long felt in the business world is this: there is a natural diffe ...

Leadership
Support, love, and trust received in childhood nurture self-confidence, cou ...

Generation Z: Not Just a Mirror, but ...
One of the most frequent complaints in today’s business world is: “Young em ...

A New Era in Business with Artificia ...
The Industrial Revolution began with steam. Then came electricity, computer ...

The New Face of Entrepreneurship: Wo ...
The new generation of entrepreneurship is no longer solely profit-driven; i ...

Understood Employees Contribute and ...
In the corporate world, we often hear statements like: “They’re talented, b ...

The Silent Power of Corporate Succes ...
In today's business world, organizations operate in an environment shaped b ...

Customer Relations and Training in B ...
Bancassurance, a business model in which banks market insurance products to ...

What Awaits the Business World? A St ...
Digitalization is no longer just a technological trend but a necessity for ...

Digital Transformation in Conflict M ...
Conflict is a reality we encounter in all aspects of life. Whether at home, ...

Neova Sigorta Leadership Certificate ...
Neova Sigorta Leadership Certificate Program from a Coaching Perspective ha ...

We have completed our Kafein Technol ...
We have completed our Kafein Technology Strategic Leadership Training.

We completed our training at the Ist ...
We completed our training at the Istanbul City Council "The Budget is Yours ...

The Road to Success: Market Dynamics ...
In today’s rapidly changing market conditions, the importance of management ...

Leadership in the Digital Age: A New ...
Leadership in the digital age requires embracing continuous learning, innov ...

Mastering Risk Management
Mastering risk management is not merely an option for businesses but a nece ...

International Banking in Germany: A ...
Germany, with its strong industrial structure, high-technology products, an ...
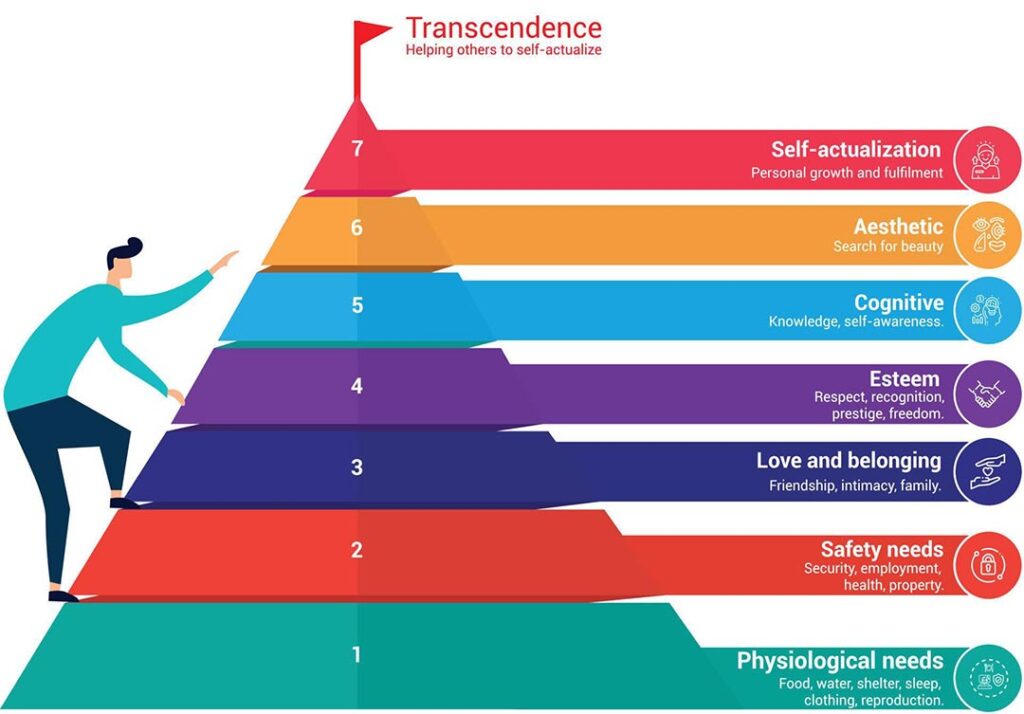
Leadership and Maslow's Hierarchy of ...
Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a fundamental psychological theory u ...

Leadership and Sustainability of Org ...
Today's business world is characterized by continuous change, technological ...

The Importance of Coaching Skills f ...
The Importance of Coaching Skills for LeadersCoaching skills are essenti ...

Fintech in Turkey: The Rise of Finan ...
Fintech in Turkey: The Rise of Financial Technology

Bancassurance
Bancassurance is a business model that is among the financial services offe ...

Banking and Frankfurt
When the banking and finance sector in Europe is analyzed, it is seen that ...

Digital Banking and Germany
Digital banking is a banking service where customers can do their banking o ...

Banking in Germany
Euro used since 2002 in The Eurozone, the currency of 19 EU members. There ...

Strategic Communication
Strategic communication plays a critical role in the success of an organiza ...

Importance of Supply Chain
The supply chain is a critical factor in which a company manages the flow o ...

Key to Success: Going Digital
Digital transformation is a transformation process that aims to increase th ...

Welfare
Poverty and inequality are one of the biggest challenges the current societ ...

ChatGPT
ChatGPT, developed by the OpenAI company known for its work and research in ...

What is Emotional Intelligence and w ...
Emotional intelligence (also known as emotional quotient or EQ) is the abil ...

The Importance of Women's Employment ...
Women's participation in the workforce is closely related to the level of d ...

Digital Banking II – Digital Banking ...
A serious step taken for the spread of “digital banking” in Turkey, providi ...

The Perception of Morality within Ma ...
If everybody in the world jumped out of a window, would you? This question ...
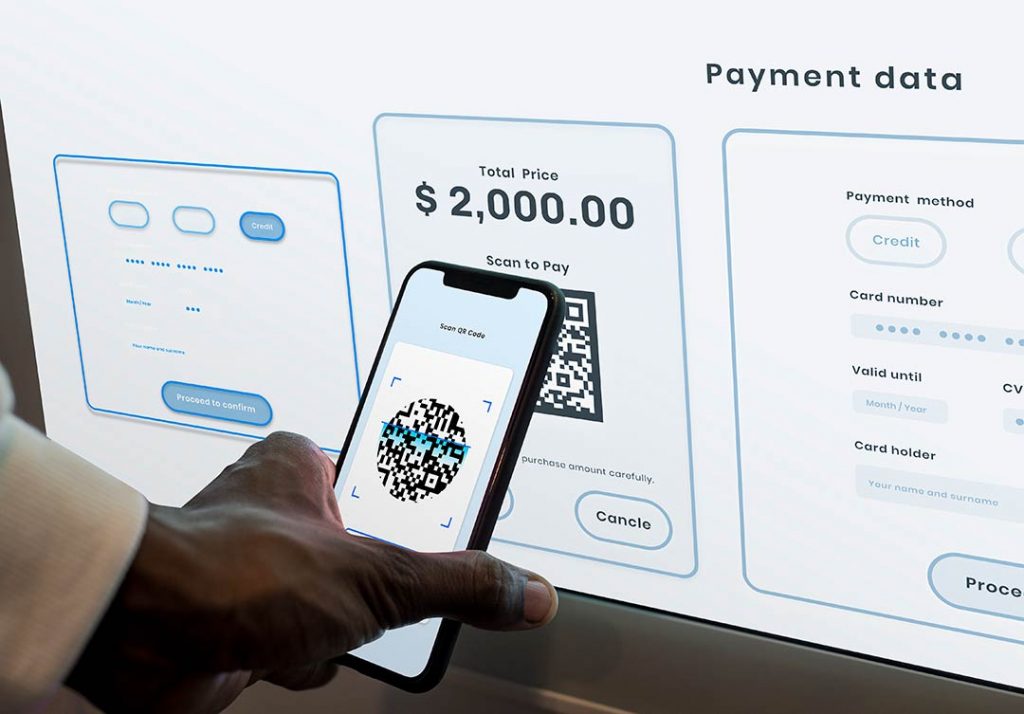

Digital Banking
Digital banking is a banking technology that offers customers the opportuni ...

Banking, Artificial Intelligence and ...
We have heard the concepts of metaverse, artificial intelligence and machin ...

Banka Şube Müdürünün El Kitabı 2. Ba ...
Banka Şube Müdürünün El Kitabı 2. Baskı Çıktı – Çiğdem Güven

Green Asset Ratio
Sustainable finance has an important place among the investments made for t ...

Servant Leadership
There is an effective form of management that we often hear about today: se ...

Sustainability In The Global Banking ...
Before Covid-19 wreaked havoc on the world’s economies, the global banking ...

Banka Şube Müdürünün El Kitabı – Çiğ ...
Banka Şube Müdürünün El Kitabı – Çiğdem Güven

Revolution of Digital Banking
With the European Central Bank considering to investigate for a digital cur ...

The Global Leadership Program
The Global Leadership Program held on October 22, 2021 was completed.

Taking Action and Making Decisions i ...
Uncertainty is the fact that an event is not within the framework of certai ...

Türkisch-Deutsche Industrie-und Hand ...
Türkisch-Deutsche Industrie-und Handelskammer

Hacettepe University Entrepreneurshi ...
Hacettepe University Entrepreneurship and Investment Society

Wind of Change
Change is an important concept that must be managed for employees at all le ...

Organizational Justice
“What is justice? Giving water to trees. What is injustice? To give water t ...

Open Banking
Digital transformation has started to show its effects in every aspect of o ...

Digital Literacy And Corporate Life
There are many innovations that managers and employees need to follow in or ...

Financial Literacy
The words money and economy are two important concepts that have a great pl ...

Sustainability and Bank
The solutions we have found to our various needs throughout history and ada ...

Adaptability, Flexibility and Leader ...
Being able to adapt to changing conditions is very, very important not only ...

Creativity and Leadership Relationsh ...
The world is getting more competitive every day. For this reason, the servi ...

Competitive Analysis and Banking Sec ...
Competition analysis requires you to examine your direct and indirect compe ...

Delegation in Management
The statements "two heads are better than one" or "teamwork makes the dream ...

Climate Change
All creatures evolve to best adapt to environmental impacts. Those who are ...

Change of Banking Service Channels i ...
Global crises such as the pandemic, force the existing structures to change ...

Innovation
It is undeniable that innovation has a very important place in today's worl ...

Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is no longer just something specific to science fic ...

Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is the process of starting a new business that incorporate ...
Global Leadership
The world is changing day by day and the information we have today is out o ...

Resilience and Leadership
We encounter many events in life that cause us difficulties and stress. How ...

Entrepreneurial Spirit for Leaders
Why is important for success? The conventional perception of entrepreneursh ...

The webinars for Team Motivation, Cr ...
The webinars for Team Motivation, Crisis Management, Digital Leadership and ...

Finance Leadership in a Pandemic
Crises bring along a period in which institutions need to review their fina ...

Crisis Management
Crisis is a state of tension that puts the existence and goals of an organi ...

Strategic Leadership and Pandemic
Strategic Leader is the person who sets the roadmap to achieve the ultimate ...

Awareness, Appreciation, Success
It is very important for a person to recognize himself, discover his power ...

Woman and Career
People who are raised by unemployed mothers have a mother model in their mi ...

Conflict Management
In the broadest sense, conflict is disagreement between two or more people ...

Leading with Kindness
Kindness is an important virtue. Kindness in all areas of life makes relati ...

Smart Meetings
Meeting management is the process of managing all stages and components of ...

Negotiation Management
Negotiation is defined as a dialogue aimed at reaching a common and benefic ...

Virtual Leadership
The repercussions of the digitalization process in business life were sprea ...

Manager and Patience
Patience is an important concept in management. Patience is active, not pas ...

Being All Ears
Human beings differ from other creatures in their way of communicating. Com ...

Networking
The fact that managers in the corporate world act with awareness of network ...

Asking Strong Questions
For managers, asking a strong question is an important skill. Managers, who ...

Managing Yourself
The manager at work is in communication with the other parts of the busines ...

Mental Immunity
In the fight against Coronavirus (Covid-19) pandemic, knowledge and awarene ...
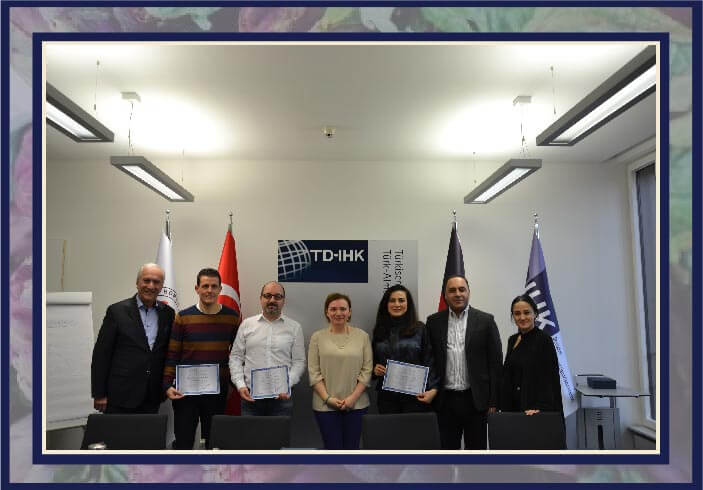

Coaching and Effective Communication ...
Coaching and Effective Communication Training TD-IHK

"On Coaching and Communication in Co ...
Coaching is a service that forms the basis of success stories by creating a ...

The Future of Digital Finance in the ...
The Cigdem Guven Seminars welcomed one of the most successful businesspeopl ...
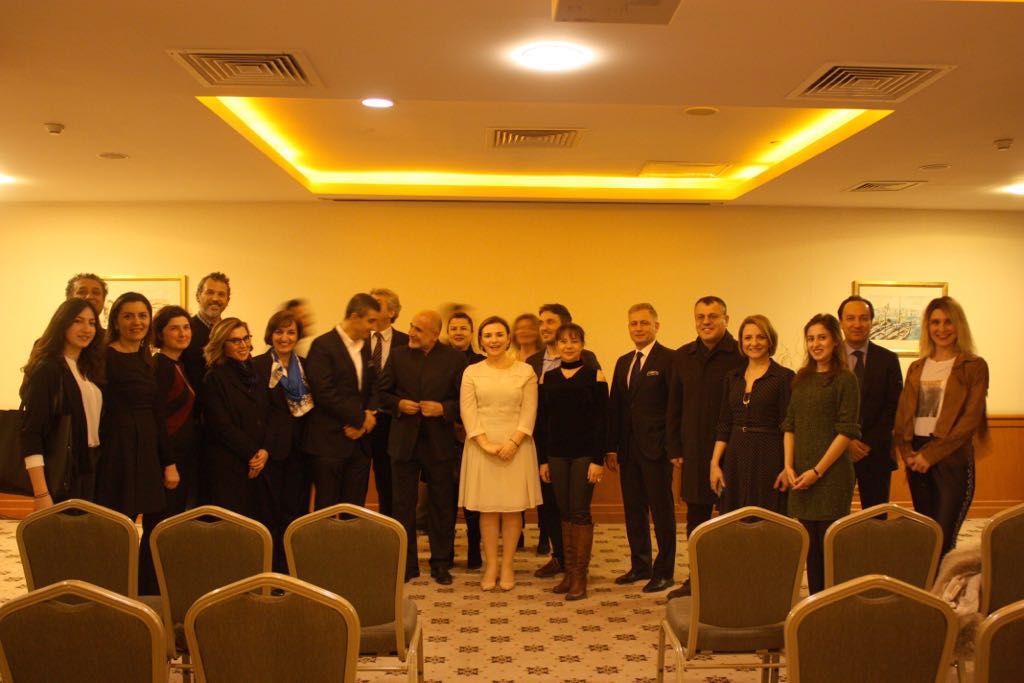

Making Life Beautiful With Plastic S ...
Çiğdem Güven Seminars, which welcomes the specialist and inspirational spea ...
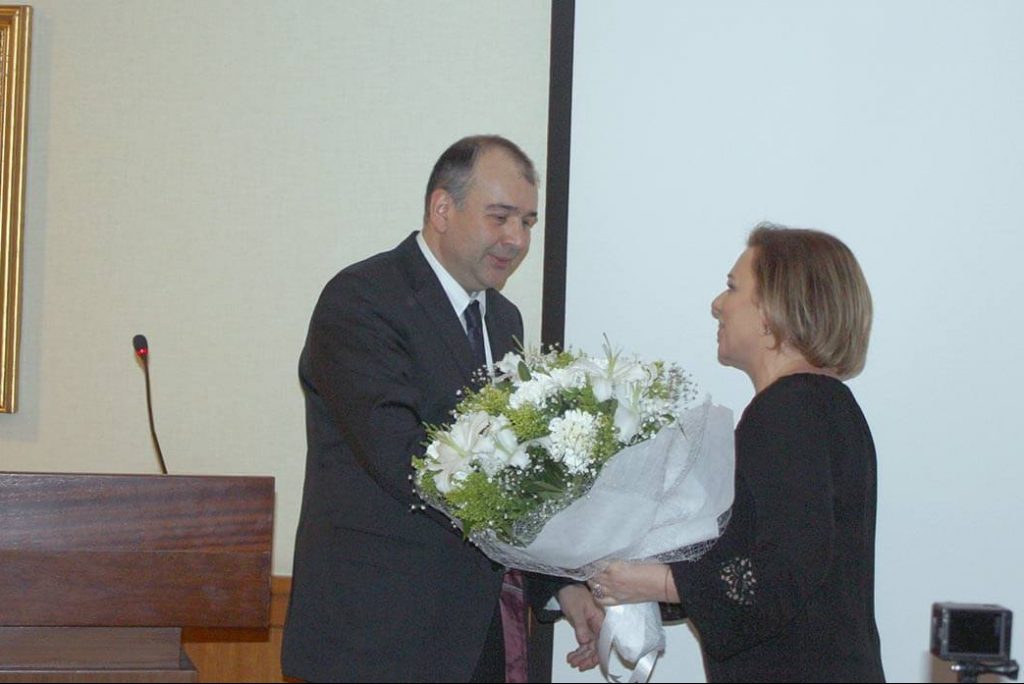

The Secrets of How Our Brains Works ...
The seminar started with the opening speech made by Cigdem Guven, and then ...
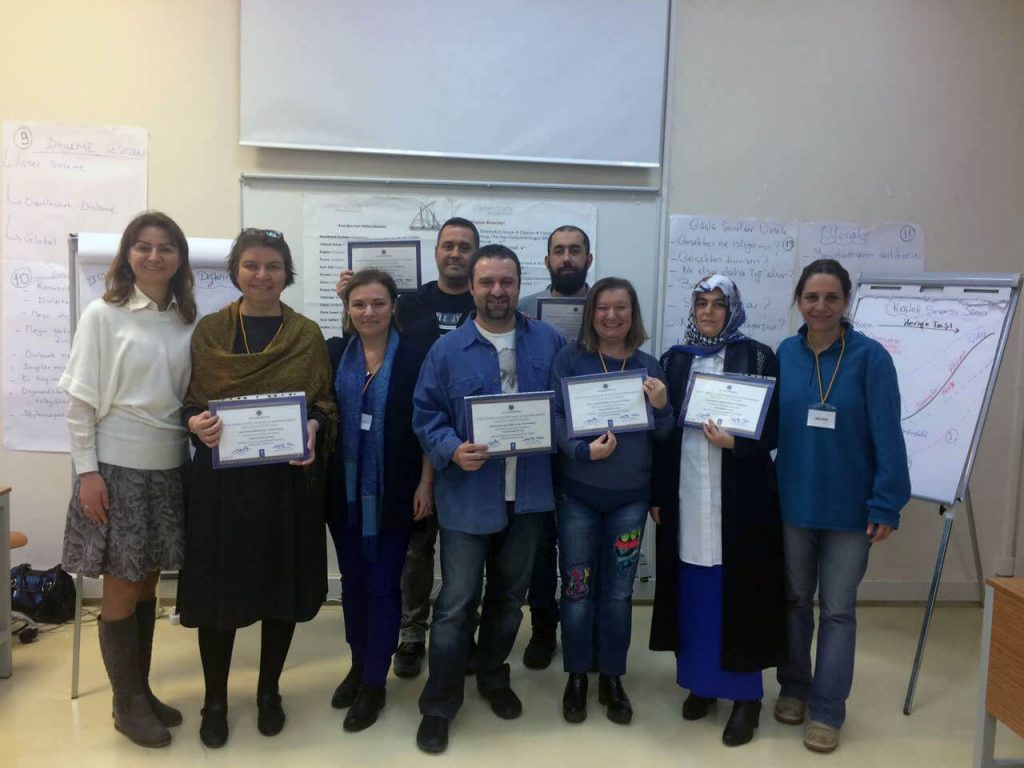

Yildiz Technical University Coaching ...
Those who want to make a professional entry to the personal development sec ...
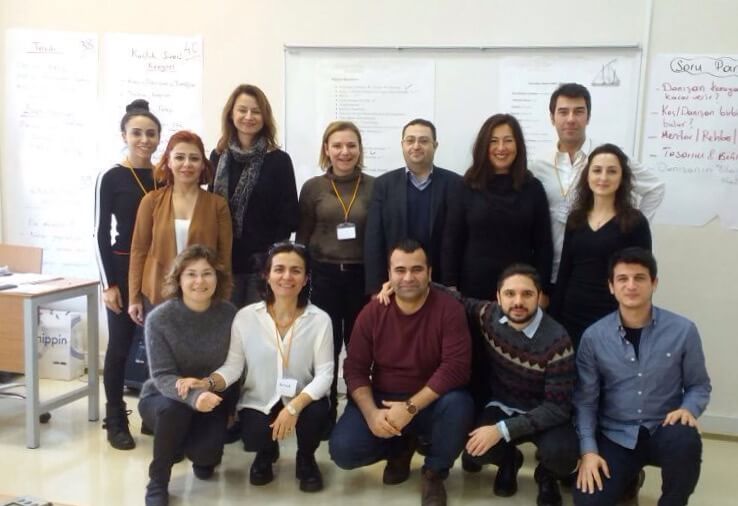

Yildiz Technical University Coaching ...
Yıldız Technical University’s Coaching Certification Program aims to fulfil ...
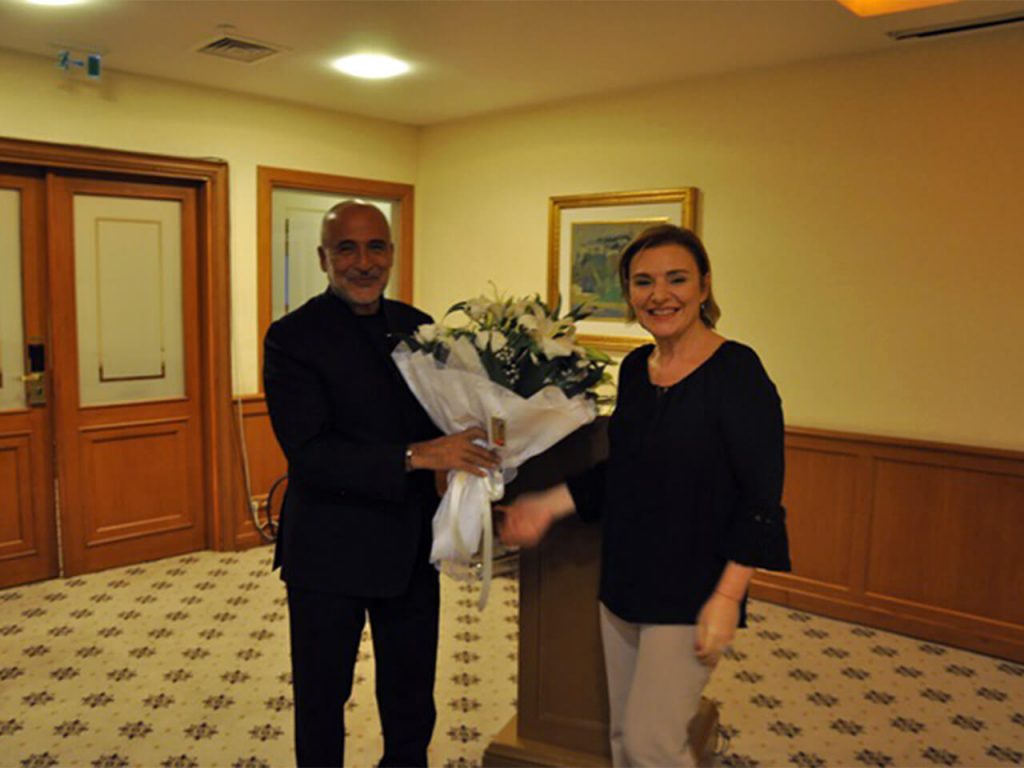

Making Life Beautiful With Plastic S ...
Bringing different point of views with its successful and authentic speaker ...
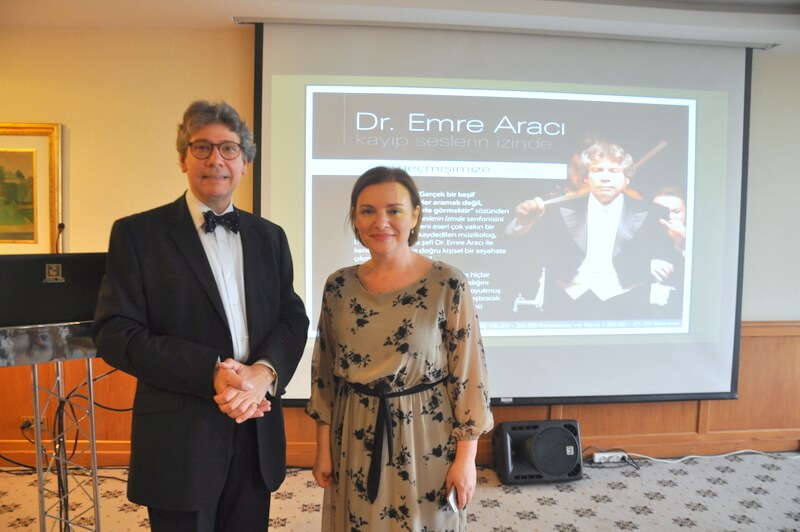

In Search of Lost Sounds – A Persona ...
Aiming to provide different perspectives about life with its inspiring gues ...
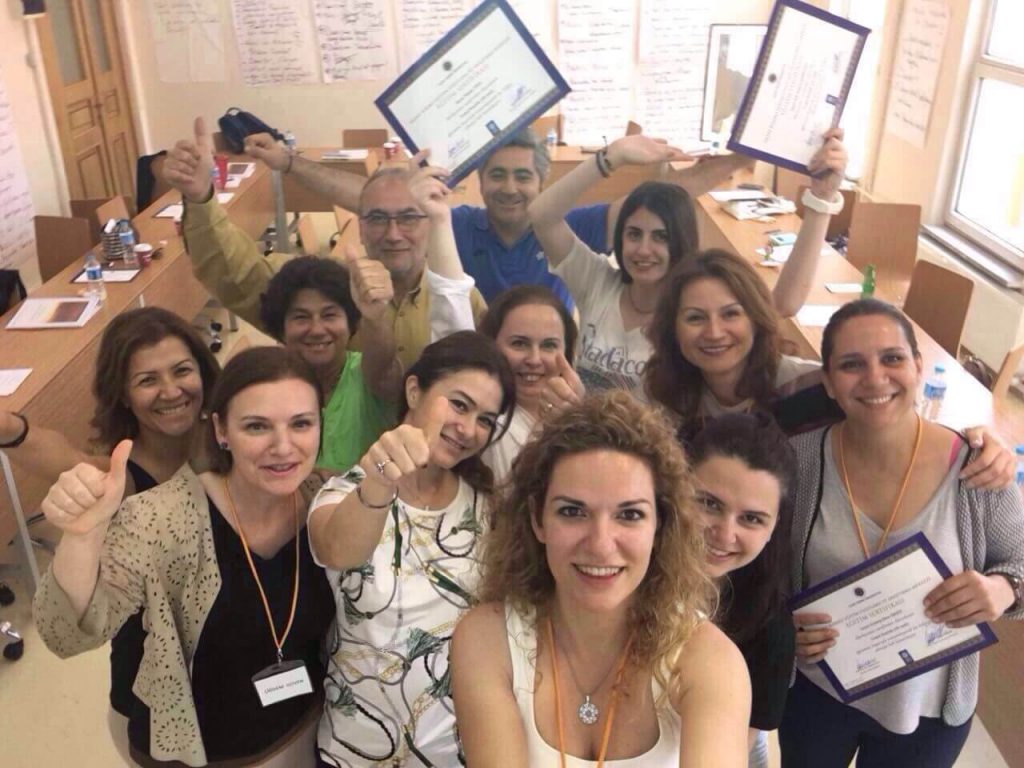

Yıldız Technical University Coaching ...
In addition to having provided leading senior executives with individualize ...

To Succeed is to Discover Yourself, ...
Çiğdem Güven, who has been bringing many well-known experts of different ar ...

Peace of Mind With Spiritualist Yoge ...
Providing individualized coaching services to leading senior executives wit ...

Dealing With Life’s Storms, With Yog ...
Çiğdem Güven, who has been bringing many well-known experts of different ar ...

Spiritual Intelligence With Yogesh S ...
Aiming to provide different perspectives about life with its inspiring gues ...

