When the banking and finance sector in Europe is analyzed, it is seen that the city of Frankfurt stands out as the financial center of Germany. It is one of the most important locations for banks and financial services in continental Europe and is critical to the economic strength of the FrankfurtRheinMain region.
The number and importance of credit institutions, stock exchanges, financial intermediaries and specialist scientific institutions in Frankfurt are surpassed in Europe only by London. However, with the Brexit process, it is seen that the gap between the two cities started to close rapidly in favor of Frankfurt. In the global ranking of financial centers, New York, London, Tokyo and Frankfurt make up the top four.
Most of the financial players in Germany are concentrated in Frankfurt. While the European Central Bank (ECB), Bundesbank , German Stock Exchange and EIOPA have their headquarters in Frankfurt, there are also many venture and business development agencies. Together with neighboring universities and technical colleges, Frankfurt is developing into a highly financially competent science center.
The ECB is tasked with guaranteeing the purchasing power and price stability of the Euro, the common currency of the Eurozone. The Eurozone consists of 15 European Union countries that have introduced the Euro since 1999. Deutsche The Bundesbank is the central bank of the Federal Republic of Germany and is responsible for the monetary policy of the Eurosystem. Other core business areas include the financial and currency system, banking supervision, cashless payments and cash. The ECB (European Central Bank) is an institution based in Frankfurt that manages the monetary policy of the euro area. As of 2021, the total balance sheet of the ECB is around 7 trillion Euros.
The Federal Financial Supervisory Authority ( BaFin ) acts in the public interest of banks and financial service providers, insurance and securities trading. Its main objective is to guarantee a functioning, stable, honest and sustainable German financial system. EIOPA (European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Agency) is an independent insurance and occupational pensions body and advises the European Commission. Even after the financial crisis, the Frankfurt financial center has not lost any of its attractiveness.
Frankfurt is known as the financial center of Germany and many banks have their headquarters or branches here. There are approximately 200 banks and financial institutions in Frankfurt. The vast majority of these banks are private or commercial banks. The headquarters of some banks located in Frankfurt are:
- Deutsche Bank
- Commerzbank
- DZ Bank
- KfW Bankengruppe
- Helaba ( Landesbank Hesse-Thuringia )
Among international banks, banks with branches or headquarters in Frankfurt include:
- JPMorgan Chase
- Citibank
- Goldman Sachs
- Morgan Stanley
- HSBC
- Society General
- UBS
- Credits Suisse
- ING Group
- BNP Paribas
According to 2020 data, the market shares among the largest banks in Germany are as follows:
- Deutsche Bank: 5.5 %
- Commerzbank : 2.8 %
- KfW Bankengruppe : 1.8 %
- DZ Bank: 1.7%
It is known that the most popular place of business preferred by companies that are internationally active in the financial sector is the German financial center. The Banking Committee promotes awareness in the financial sector, as it recognizes that the success of the Frankfurt financial center, and thus its reputation, is linked to the German financial center. This balances all players in the Main region. It not only balances classical banks’, comprehensive financial institutions but also affects new players whose importance is increasing for the financial sector.
The recent turmoil in the financial markets has not only affected the players in the markets, but also attracted the attention of various regulatory institutions around the world. This situation has led to intense discussions on the depth of possible regulatory interventions. The main event is to implement an effective regulatory architecture. The most recent example in this regard is the European Parliament's Finance Committee's call to gather all future European financial audits in Frankfurt.
Frankfurt is a highly successful financial center competing with globally networked exchanges. Many strengths characterize this financial center. Deutsche Börse surrounds the world and is a global network that must continue to expand. This does not change its vital link with the Frankfurt financial center. On the one hand, Deutsche Börse's success gives the Frankfurt region an international reputation as well as sustainable economic stability and secure jobs. On the other hand, Deutsche Börse will not be able to cope with the difficulties of global competition without it, because it draws strength from this region.
Besides financial capital, human capital also plays a decisive role in the competition between metropolises. House of Finance and Frankfurt School of Finance and Management form an intellectual infrastructure that can compete on equal terms with the financial centers of London and Paris. Frankfurt is synonymous with common sense. Frankfurt's financial sector, unlike other financial centers, has always maintained close ties to the real economy. This is one of the reasons why the metropolis on Main never showed waves of extremism or layoffs like other international financial centers, even at the height of the financial crisis. The actors in the Frankfurt financial center act on the belief that the most important task of a financial center is to combine long-term capital requirements with long-term investment requirements to support economic growth. Relevant actors should also continue to focus on this function.
The European Central Bank has a great role in making Frankfurt an international financial center. The establishment of the European Central Bank (ECB) gave significant impetus to which the city as a whole benefited. Frankfurt has always been a very open city and, thanks to the ECB, it has become perhaps the most European of all cities.
German SMEs are extremely popular among banks. Medium-sized businesses have been seen as a classic line of business for cooperative banks and savings banks for years. However, medium-sized companies are now at the center of the competition. Regulations, lost business models, a return to domestic markets triggered by the financial market and government debt crisis, and the strength of the German economy make this possible. In short, the return to the real economy allows banks to give small and medium-sized enterprises the attention they deserve due to their superior position in the country's economy.
Developing capital markets in terms of alternative financing sources and risk management for medium-sized large companies is an issue that has gained importance recently. The interest of companies in diversifying their investors or in alternative financing sources has been revived, especially with the developments experienced in the past crisis years. Alternative financing instruments are seen as an important option for investors who want to increase their equity or for companies looking for new investors by issuing bonds. In this context, securities, which are an interesting alternative especially for medium-sized companies and investors, are accepted as a financing tool close to the capital market.
This increasing capital market demand shows how important it is for an internationally important financial center like Frankfurt. Frankfurt is a financial center that plays a leading role worldwide and is the national champion of Germany. Around 75,000 people are employed in 260 credit institutions, including the four largest German banks and around 200 foreign banks from 40 countries.
The Frankfurt Chamber of Industry and Commerce (IHK Frankfurt) and its banking committee play an important role in the Frankfurt financial center. Because most of the major financial institutions represented here work. IHK Frankfurt and its banking committee are known for their strategies aimed at making the Frankfurt financial center the supervisory center of European financial markets. These two organizations also support the external image and marketing of the Frankfurt financial center. They collaborate on the creation of a successful trademark 'Frankfurt Main Finance' for the financial center. Not giving up is one of the decisive factors for the future of the financial center, where the priority of all established financial centers in the world, including Frankfurt, is constantly questioned. This is also demonstrated by the Global Financial Centers Index (GFCI): 24 of the 50 financial centers listed in 2007 were in Europe, compared to just 34 out of 77 in 2012. However, this is a dynamic advantage for Frankfurt, as it has emerged as a reliable and knowledgeable partner for the development of financial centers in emerging markets. Foreign investors have a clear idea of what the Frankfurt financial center has to offer.
Share:
Related Articles

Understood Employees Contribute and ...
In the corporate world, we often hear statements like: “They’re talented, b ...

The Silent Power of Corporate Succes ...
In today's business world, organizations operate in an environment shaped b ...

Customer Relations and Training in B ...
Bancassurance, a business model in which banks market insurance products to ...

What Awaits the Business World? A St ...
Digitalization is no longer just a technological trend but a necessity for ...

Digital Transformation in Conflict M ...
Conflict is a reality we encounter in all aspects of life. Whether at home, ...

The Road to Success: Market Dynamics ...
In today’s rapidly changing market conditions, the importance of management ...

Leadership in the Digital Age: A New ...
Leadership in the digital age requires embracing continuous learning, innov ...

Mastering Risk Management
Mastering risk management is not merely an option for businesses but a nece ...

International Banking in Germany: A ...
Germany, with its strong industrial structure, high-technology products, an ...
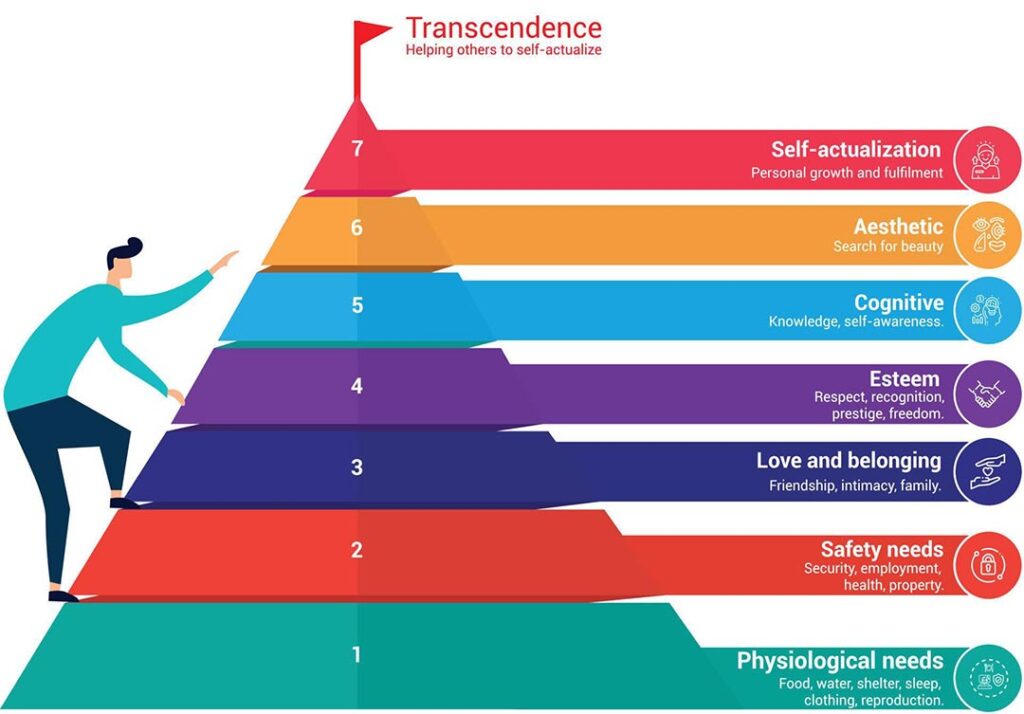
Leadership and Maslow's Hierarchy of ...
Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a fundamental psychological theory u ...

Leadership and Sustainability of Org ...
Today's business world is characterized by continuous change, technological ...

The Importance of Coaching Skills f ...
The Importance of Coaching Skills for LeadersCoaching skills are essenti ...

Fintech in Turkey: The Rise of Finan ...
Fintech in Turkey: The Rise of Financial Technology

Bancassurance
Bancassurance is a business model that is among the financial services offe ...

Banking and Frankfurt
When the banking and finance sector in Europe is analyzed, it is seen that ...

Digital Banking and Germany
Digital banking is a banking service where customers can do their banking o ...

Banking in Germany
Euro used since 2002 in The Eurozone, the currency of 19 EU members. There ...

Strategic Communication
Strategic communication plays a critical role in the success of an organiza ...

Importance of Supply Chain
The supply chain is a critical factor in which a company manages the flow o ...

Key to Success: Going Digital
Digital transformation is a transformation process that aims to increase th ...

Welfare
Poverty and inequality are one of the biggest challenges the current societ ...

ChatGPT
ChatGPT, developed by the OpenAI company known for its work and research in ...

What is Emotional Intelligence and w ...
Emotional intelligence (also known as emotional quotient or EQ) is the abil ...

The Importance of Women's Employment ...
Women's participation in the workforce is closely related to the level of d ...

Digital Banking II – Digital Banking ...
A serious step taken for the spread of “digital banking” in Turkey, providi ...

The Perception of Morality within Ma ...
If everybody in the world jumped out of a window, would you? This question ...
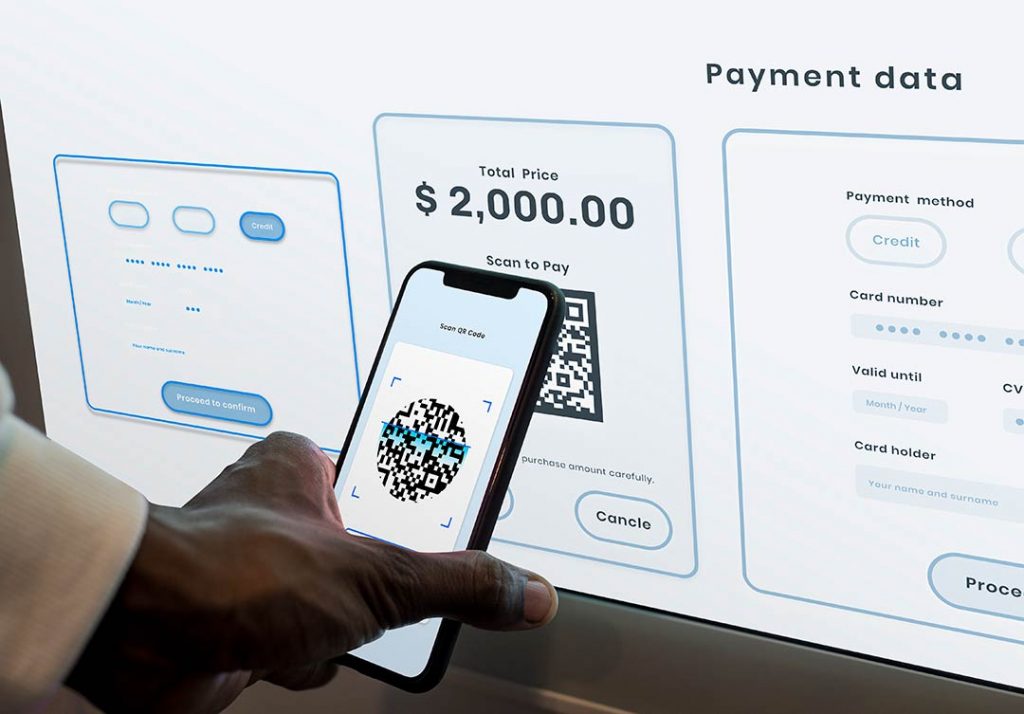

Digital Banking
Digital banking is a banking technology that offers customers the opportuni ...

Banking, Artificial Intelligence and ...
We have heard the concepts of metaverse, artificial intelligence and machin ...

Green Asset Ratio
Sustainable finance has an important place among the investments made for t ...

Servant Leadership
There is an effective form of management that we often hear about today: se ...

Sustainability In The Global Banking ...
Before Covid-19 wreaked havoc on the world’s economies, the global banking ...

Revolution of Digital Banking
With the European Central Bank considering to investigate for a digital cur ...

Taking Action and Making Decisions i ...
Uncertainty is the fact that an event is not within the framework of certai ...

Wind of Change
Change is an important concept that must be managed for employees at all le ...

Organizational Justice
“What is justice? Giving water to trees. What is injustice? To give water t ...

Open Banking
Digital transformation has started to show its effects in every aspect of o ...

Digital Literacy And Corporate Life
There are many innovations that managers and employees need to follow in or ...

Financial Literacy
The words money and economy are two important concepts that have a great pl ...

Sustainability and Bank
The solutions we have found to our various needs throughout history and ada ...

Adaptability, Flexibility and Leader ...
Being able to adapt to changing conditions is very, very important not only ...

Creativity and Leadership Relationsh ...
The world is getting more competitive every day. For this reason, the servi ...

Competitive Analysis and Banking Sec ...
Competition analysis requires you to examine your direct and indirect compe ...

Delegation in Management
The statements "two heads are better than one" or "teamwork makes the dream ...

Climate Change
All creatures evolve to best adapt to environmental impacts. Those who are ...

Change of Banking Service Channels i ...
Global crises such as the pandemic, force the existing structures to change ...

Innovation
It is undeniable that innovation has a very important place in today's worl ...

Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is no longer just something specific to science fic ...

Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is the process of starting a new business that incorporate ...
Global Leadership
The world is changing day by day and the information we have today is out o ...

Resilience and Leadership
We encounter many events in life that cause us difficulties and stress. How ...

Entrepreneurial Spirit for Leaders
Why is important for success? The conventional perception of entrepreneursh ...

Finance Leadership in a Pandemic
Crises bring along a period in which institutions need to review their fina ...

Crisis Management
Crisis is a state of tension that puts the existence and goals of an organi ...

Strategic Leadership and Pandemic
Strategic Leader is the person who sets the roadmap to achieve the ultimate ...

Awareness, Appreciation, Success
It is very important for a person to recognize himself, discover his power ...

Woman and Career
People who are raised by unemployed mothers have a mother model in their mi ...

Conflict Management
In the broadest sense, conflict is disagreement between two or more people ...

Leading with Kindness
Kindness is an important virtue. Kindness in all areas of life makes relati ...

Smart Meetings
Meeting management is the process of managing all stages and components of ...

Negotiation Management
Negotiation is defined as a dialogue aimed at reaching a common and benefic ...

Virtual Leadership
The repercussions of the digitalization process in business life were sprea ...

Manager and Patience
Patience is an important concept in management. Patience is active, not pas ...

Being All Ears
Human beings differ from other creatures in their way of communicating. Com ...

Networking
The fact that managers in the corporate world act with awareness of network ...

Asking Strong Questions
For managers, asking a strong question is an important skill. Managers, who ...

Managing Yourself
The manager at work is in communication with the other parts of the busines ...

Mental Immunity
In the fight against Coronavirus (Covid-19) pandemic, knowledge and awarene ...

